Step 1 Establish and verify
connectivity to the Internet
This ensures the computer has an IP address.
Step 2 Access the command prompt
Use the Start menu to open the Command Prompt
window. Press Start, type Run then type cmd
which stands as Command Prompt
Step 3 ping the IP address of
another computer
In the window, type ping, a space, and the IP address of a computer recorded in the
previous lab.
Ping uses the ICMP echo request and echo reply feature to test physical
connectivity. Since ping reports on four attempts, it gives an indication of
the reliability of the connection. Look over the results and verify that the
ping was successful. Is the ping successful? Yes.
If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting.
If a second networked computer is available, try to ping the IP address
of the second machine.
Note the results.
Step 4 ping the IP address of
the default gateway
Try to ping the IP address of the default
gateway if one was listed in the last exercise. If the ping is successful, it
means there is physical connectivity to the router on the local network and
probably the rest of the world.
Step 5 ping the IP address of a
DHCP or DNS servers
Try to ping the IP address of any DHCP and/or DNS servers listed in the
last exercise.
If this works for both server and they are not in the network,
what does this indicate?
The 2 are not in the same network but have the same DNS Server.
Was the ping successful? Yes.
If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting.
Step 6 ping the Loopback IP
address of this computer
Type the following command: ping 127.0.0.1
The 127.0.0.0 network is reserved for loopback testing. If the ping is
successful, then TCP/IP is properly
installed and functioning on this computer.
Was the ping successful? Yes
If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting.
Step 7 ping the hostname of
another computer
Try to ping the hostname of the computer that was recorded in the
previous lab.
If the ping is successful, it means the computer was able to resolve
the host name to an IP address. Without name resolution, the ping would have
failed because TCP/IP only understands valid IP addresses, not names.
If the ping was successful, it means that connectivity and discovery of
IP addresses can be done with only a hostname. In fact, this is how many early
networks communicated. If successful, then ping a hostname also shows that
there is probably a WINS server working on the network. WINS servers or a local
“lmhosts” file resolve computer host names to IP addresses. If the ping fails,
then chances are there is no NetBIOS name to IP addresses resolution running.
Step 8 ping the Google web site
Type the following command: ping www.google.com
The first output line shows the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
followed by the IP address. A
Domain Name Service (DNS) server somewhere in the network was able to
resolve the name to an IP address. DNS servers resolve domain names, not
hostnames, to IP addresses.
Without this name resolution, the ping would have failed because TCP/IP
only understands valid IP addresses. It would not be possible to use the web
browser without this name resolution.
With DNS, connectivity to computers on the Internet can be verified
using a familiar web address, or domain name, without having to know the actual
IP address. If the nearest DNS server does not know the IP address, the server
asks a DNS server higher in the Internet structure.
Step 9 ping the Microsoft web
site
Type the following command: ping www.microsoft.com
Notice that the DNS server was able to resolve the name to an IP
address, but there is no response.
Some Microsoft routers are configured to ignore ping requests. This is
a frequently implemented security measure.
ping some other domain names and record the
results. For example, ping www.msn.de
Ping www.facebook.com
ping www.tumblr.com
ping www.amazon.com
Step 10 Trace the route to the Yahoo
web site
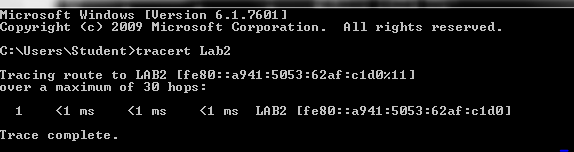
Type tracert www.yahoo.com and press
Enter.
Tracert is TCP/IP abbreviation for trace route. The preceding figure
shows the successful result when running tracert.
Each router represents a point where one network connects to another
network and the packet was forwarded through.
Step 11 Trace other IP addresses
or domain names
Try tracert on other domain names or IP addresses and record the
results. An example is
tracert www.msn.de.
tracert www.yahoo.com
Step 12 Trace a local host name
or IP address
Try using the tracert command with a local host
name or IP address. It should not take long because the trace does not pass
through any routers
Reflection
If the above steps are successful and ping or tracert can verify
connectivity with an Internet Web site, what does this indicate about the
computer configuration and about routers between the computer and the web site?
What, if anything, is the default gateway doing?
As shown, all ping and tracert was successful,and this proves that the IP Configurations are correct and then cable are properly connected to enable internet access. Ping is used to ensure proper internet connection between a web server and a computer, where the DNS configuration need to establish a successfull connection. Tracert is used to indicate the path that packets take from a computer to the internet - when accessing a website. With tracert, administrators can also monitor any problems within a network from a router that are not functioning properly .The purpose of a default gateway is to help local networks to connect to the internet.
References:
http://hnda-farah.blogspot.com/2016/04/cn-lab-exercise-2.html (for Reflection)
















No comments:
Post a Comment